linux mint下,编译boost及librime 工具经验
编译boost
下载boost
如:boost_1_82_0
https://www.boost.org/
安装boost
cd path/to/boost_1_82_0
# ./bootstrap.sh
sudo ./b2 install
编译librime
拉取源代码
git clone --recursive https://githu...
boost的字符串操作 c/c++
头文件
#include <boost/algorithm/string.hpp>
功能
字符串切割
boost::algorithm::split()
using namespace boost::algorithm;
int main()
{
std::string s = "Boost C++ Libraries";
s...
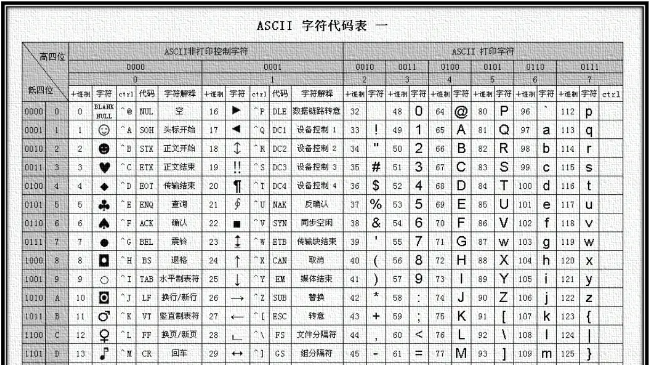
c++程序的编码与字符集的转换 c/c++
一、程序相关的编码
程序源文件编码
程序源文件编码是指保存程序源文件内容所使用的编码方案,该编码方案可在保存文件的时候自定义。
通常在简体中文windows环境下,各种编辑器(包括visual studio)新建文件缺省编码都是GB18030。
所以不特别指定的话,在windows环境下,c++源文件的编码通常为GB18030(GB18030兼容GBK)...
